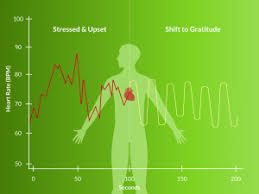
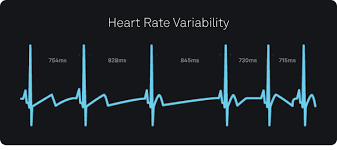
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) measures the variation in time between consecutive heartbeats. Unlike a steady heart rate, a healthy heart has slight fluctuations—these variations are controlled by the autonomic nervous system.
HRV is a powerful indicator of:
A higher HRV generally indicates better adaptability and resilience, while a low HRV may signal stress, fatigue, or underlying health issues.
What Does a Low HRV Mean?
A low HRV means your heartbeats are too regular, suggesting your body is under stress. This could be due to:
Why Is Low HRV Concerning?
-
Linked to a higher risk of heart disease
-
Associated with anxiety and depression
-
This may indicate poor recovery from exercise
-
Can reflect autonomic nervous system dysfunction
Causes of Low HRV
Several factors contribute to decreased HRV:
1. Chronic Stress
Prolonged stress keeps the body in "fight or flight" mode, suppressing HRV.
2. Poor Sleep Quality
Inadequate or disrupted sleep lowers HRV by impairing recovery.
3. Overtraining & Physical Fatigue
Excessive exercise without proper rest reduces HRV.
4. Unhealthy Diet & Dehydration
Processed foods, alcohol, and dehydration negatively impact HRV.
5. Medical Conditions
Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and autoimmune disorders can lower HRV.
How to Measure HRV Accurately
To track HRV effectively:
Ways to Improve Low HRV
1. Manage Stress
2. Optimize Sleep
3. Exercise Smartly
4. Improve Nutrition & Hydration
5. Cold Exposure & Breathing Techniques
When to Seek Medical Advice
Consult a doctor if:
-
Your HRV remains chronically low despite lifestyle changes
-
You experience heart palpitations, dizziness, or fatigue
-
You have a history of cardiovascular disease\
What Does a Low HRV FAQ
Q: Can HRV predict illness?
A: Yes, a sudden drop in HRV may indicate illness or excessive stress.
Q: Does caffeine affect HRV?
A: Yes, excessive caffeine can lower HRV by increasing stress hormones.
Q: How long does it take to improve HRV?
A: With consistent lifestyle changes, improvements can be seen in weeks.
Conclusion
A low HRV signals that your body is under stress, whether from lifestyle factors, overtraining, or health conditions. By monitoring HRV and making targeted improvements—better sleep, stress management, and balanced exercise—you can enhance your resilience and overall well-being.
Track your HRV, listen to your body, and take proactive steps toward better health!